Weaving in New Fabric
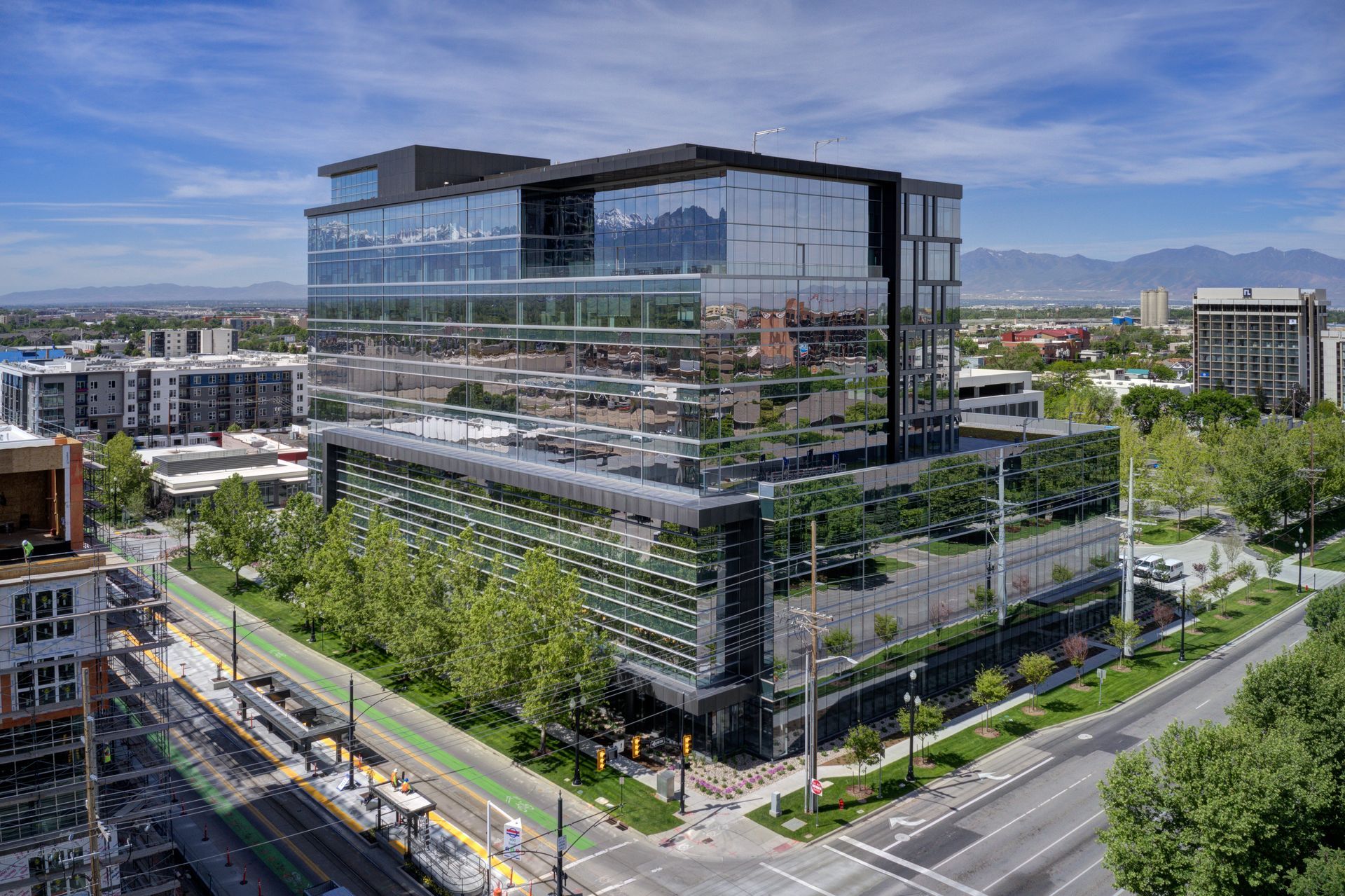
Salt Lake City continues to grow up as well as out with 650 Main’s 10-story office tower and adjoining parking garage. By Taylor Larsen
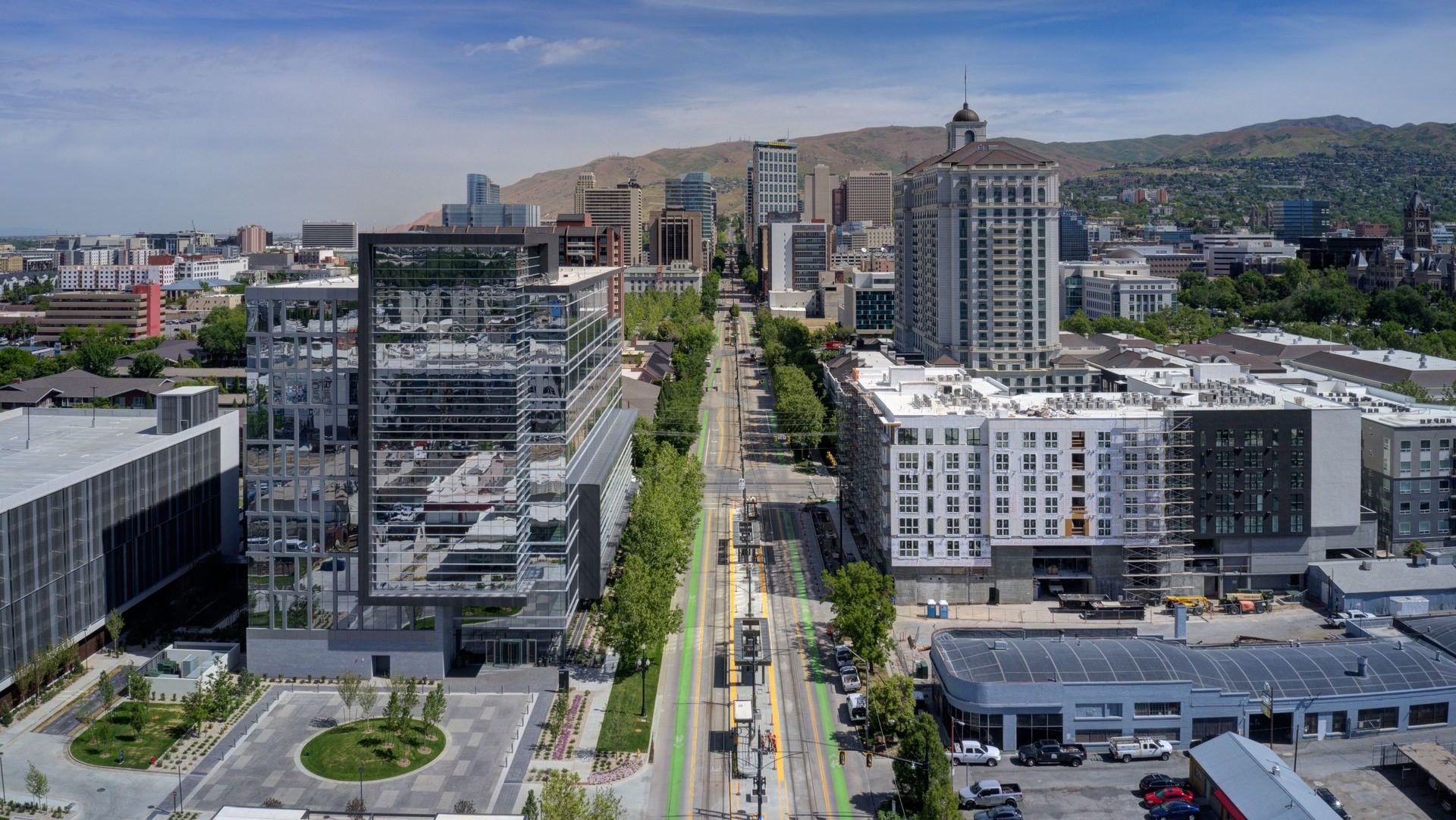

Location, location, location.
The cliche from real estate folks is true for a reason. The hustle and bustle of urban areas are where people want to be, and the newest office building to open, 650 Main, is no exception.
Forward thinking from Dennis Tarro, Executive Vice President of Houston-based developers Patrinely Group, and his team helped bring the building to life as the real estate pros looked for emerging office markets and felt like they could add something of beauty and purpose to Salt Lake’s growing south side.
With its site between 600 South and 700 South on the multi-modal Main Street, it’s just a few blocks from all three of Salt Lake’s biggest east–west vehicle connectors to I-15. That ease of access was a major selling point to Patrinely Group, especially combined with the city and state’s other amenities.
“Salt Lake City checks a lot of boxes,” he said. Whether it is the outdoor-centric and accessible lifestyle, the international airport and the Beehive State’s high quality highways, or the affordability compared to other markets, Tarro and others felt like this would be a spot where Patrinely Group could not only succeed, but create a foothold for future development and be an integral part of building up an area of an ascendent city.
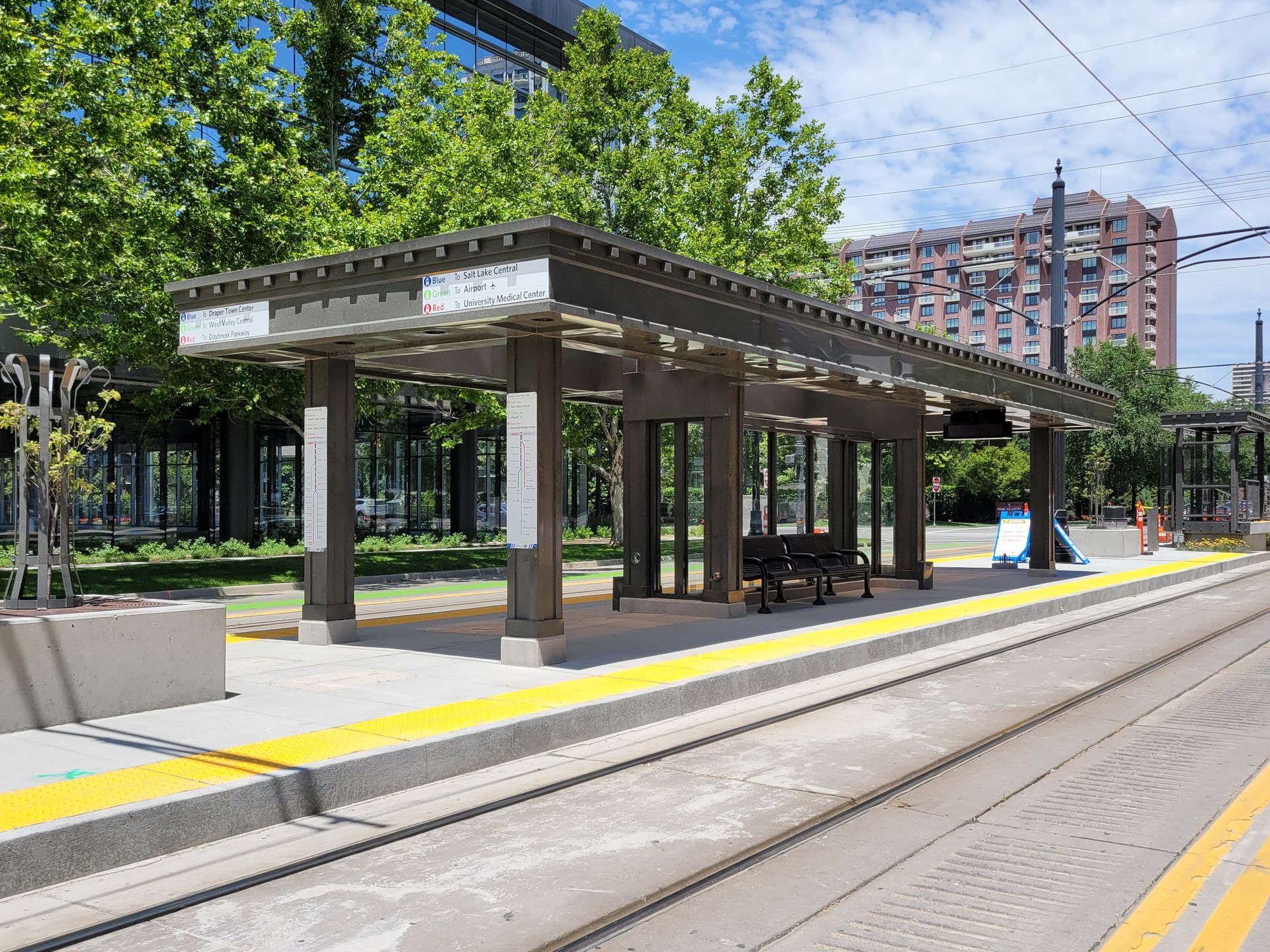
To create that foothold, Roger Soto, Design Principal for HOK’s Houston office, said that 650 Main needed to be a good urban neighbor that respected the existing downtown fabric while creating a desirable, walkable, office campus that is accessible to public transit. Accessibility grew as a group of developers near the 650 Main site, including Patrinely Group, ponied up the funds necessary to bring a TRAX Station within a minute walk from the front door.
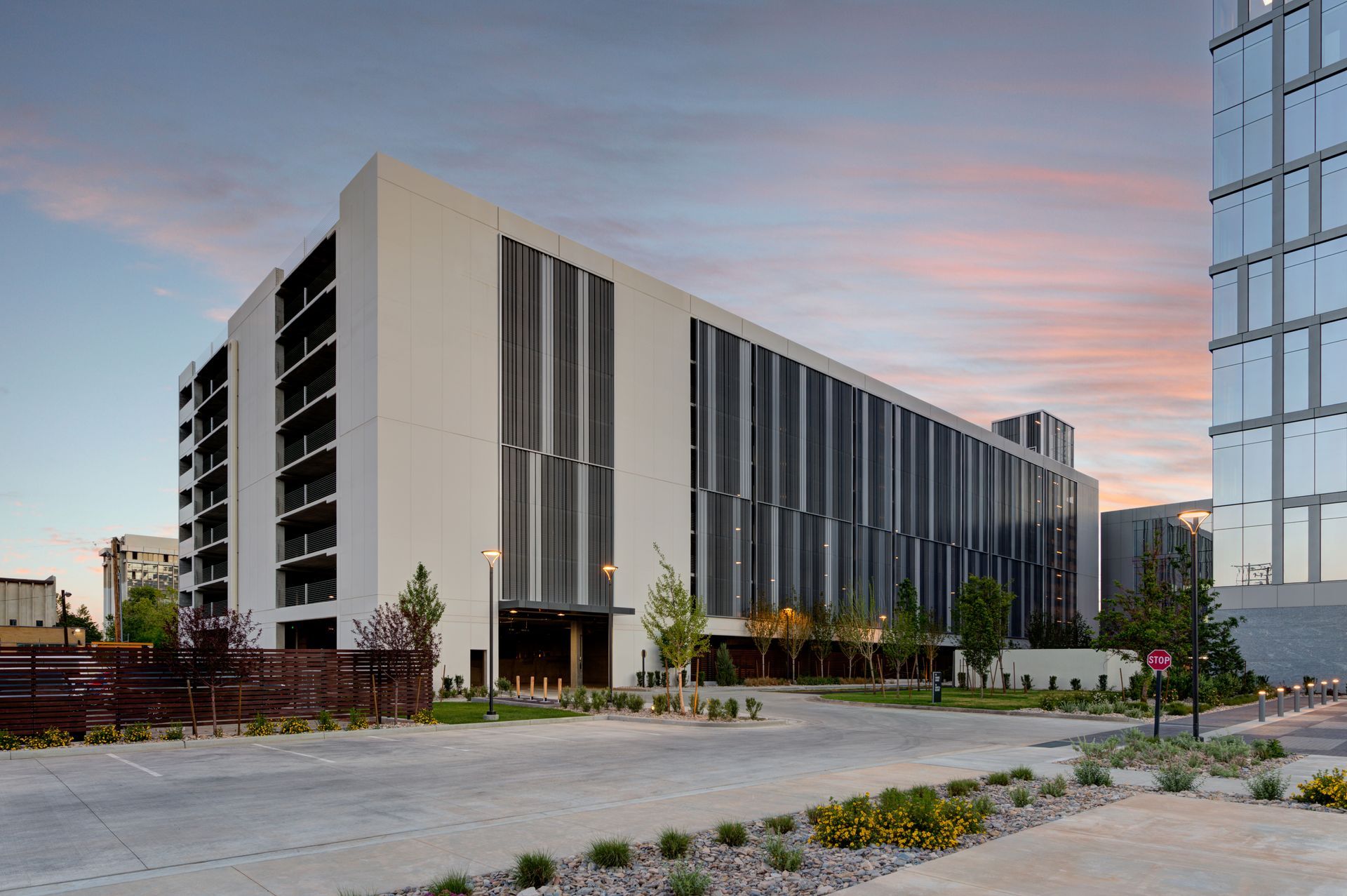
But everything has its costs beyond dollars and cents. Jeff Peterson, Vice President of Layton Construction, said staging space was at a premium. The TRAX station in the works occupied one of the sides of the construction zone while Layton and the construction teams erected 650 Main and its parking garage simultaneously. Add in “that we were [building] next to 600 South, one of the busiest streets in Salt Lake,” and the tight construction site meant their logistics work as a general contractor had to be precise.
He said that crane time was also at a premium, but one tower crane would not be enough to get the job done, and there was not enough space to fit a second tower crane. Instead, “we did it with two mobile cranes, squeezed in-between the office building and parking garage,” he said. To mitigate the potential issues from the hundreds of thousands of pounds of force exerted from the cranes, Peterson said that “a four-foot-thick base course pad made sure that the cranes were safe to operate” in a space that, today, is the office building’s lovely courtyard.
Communication between the crane operators was critical to make sure they were not picking over top of each other while ensuring everything was getting delivered and installed on time for the office building and 976-stall concrete parking garage.
“Cranes are a key part of our industry but can be dangerous if not used properly,” said Peterson. Construction crews came together for a job site huddle every morning to go over daily activities, especially crane picks, and make sure no one was working under the crane’s route.
It required another level of coordination, as the Layton team needed to be on top of material deliveries so the cranes could be most useful. Peterson mentioned that they resorted to an old school method. “We put a scheduling board in the trailer for when [crews] needed the crane,” Peterson said of the logistical success of the project. “We would referee when there was a conflict, but it worked pretty well.”
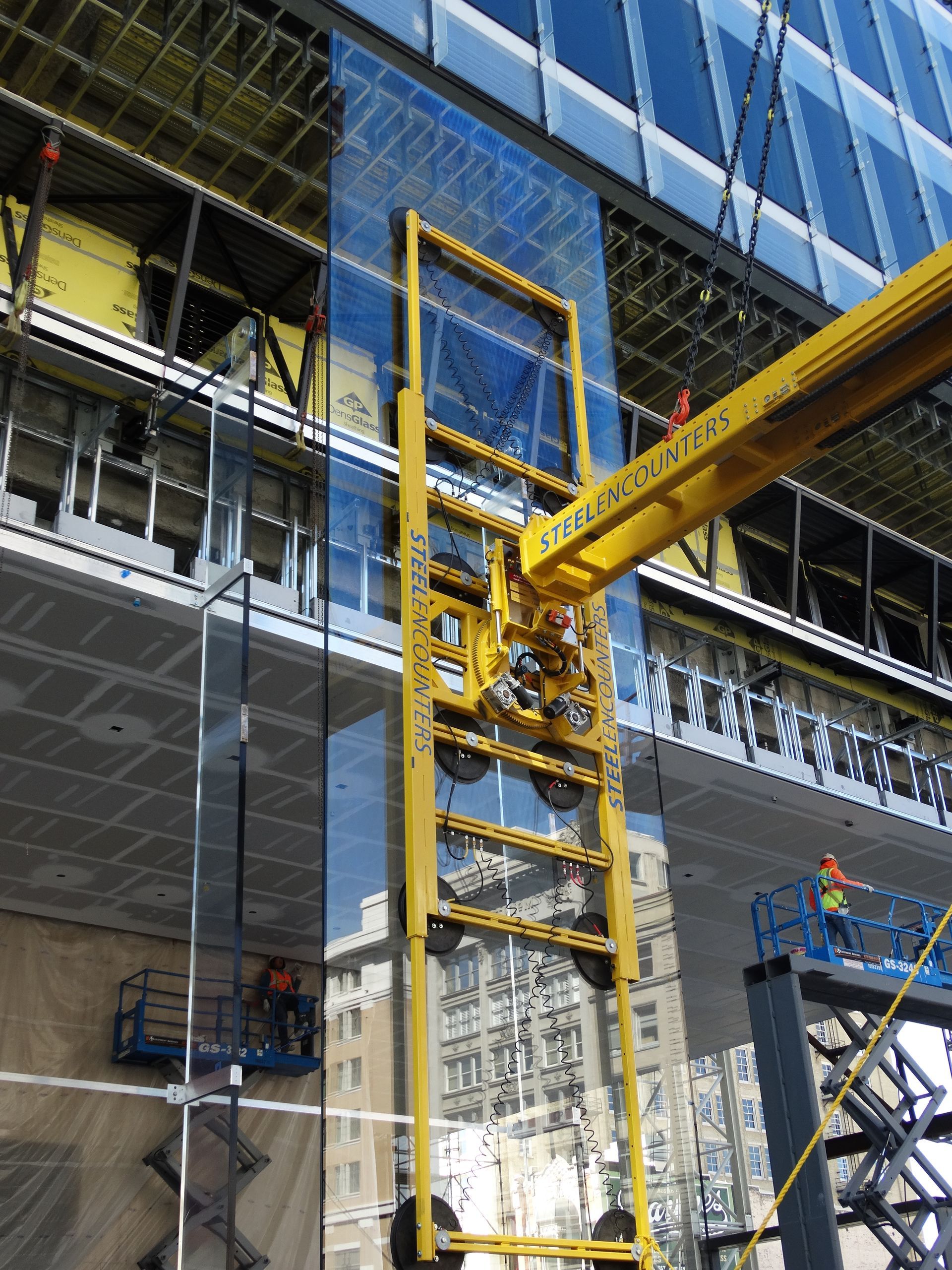
As the steel frame of the building completed, in came the glazing.
“We wanted to maximize glass,” said Bob Carnegie, Director of Architecture for HOK and Design Architect on the project. He said they worked with structural engineers to push the columns out and create cantilevers to clear the glass of any columns on this core and shell office. Floor to ceiling glass looking east to the Wasatch Mountains connects the building to Utah’s geographic majesty. Views from each of the 10 floors provide the visual connection to both the mountains and daylight—amenities that make Salt Lake and Utah so special.
Back on the ground level, the office building creates a “street wall” that engages with the street via floor to ceiling glass near 600 South's sidewalks. Soto and Carnegie explained how the building then steps back into a more standard office floor plate from the podium, a deliberate choice to respect the streets and the neighborhood, provide something architecturally compelling to energize the area, and ultimately fulfill their mission of being a good urban neighbor. Add in the nearby 4,000-plus-SF retail building that will be leased by Mexican restaurant Sol Agave, and you have a fully accessible office campus that can bring people onsite all day.
Soto described the area and the building as “fabric in the making.” And this fabric strand is modern. Metal panels function as if they were glazed into the curtain wall via the frame, even though the bent aluminum panels stick out in a non-continuous pattern.
“We worked closely with the [glazing subcontractor] JR Butler on the panels and glass to create different textures,” said Peterson of the work with their trade partner on glazing needs. Unitized and pre-fabricated panels help the façade to function as one continuous waterproofing system. Beyond utility, these framed views give tenants a lovely sight looking west.
Soto complimented how Layton suggested “a [façade] product that would fit perfectly with our goals.” Modern, efficient, fresh, forward-looking. “This is what tenants look for,” he continued.
The project’s efficiency resulted in LEED GOLD for the core and shell with high-efficiency glass and effective heating and cooling systems. Peterson said that Layton was able to recycle over 90% of their construction waste to bring another sustainability win to the project.
He was complimentary of developer Patrinely Group for their landscaping choices that will “add to the community and help with the beauty of the building.” From a bird’s eye view on the top floor, all of the new plants in their neat little rows make it seem like an entire nursery was placed on the site.
“We wanted to feel like the building and occupants weren’t sealed off from nature,” said Soto. They accomplished that via a terrace on the first setback from the ground floor plane and another terrace at the top corner of the building. The biophilic link is a unique and meaningful component of sustainability as the building creates engagement with the natural world.
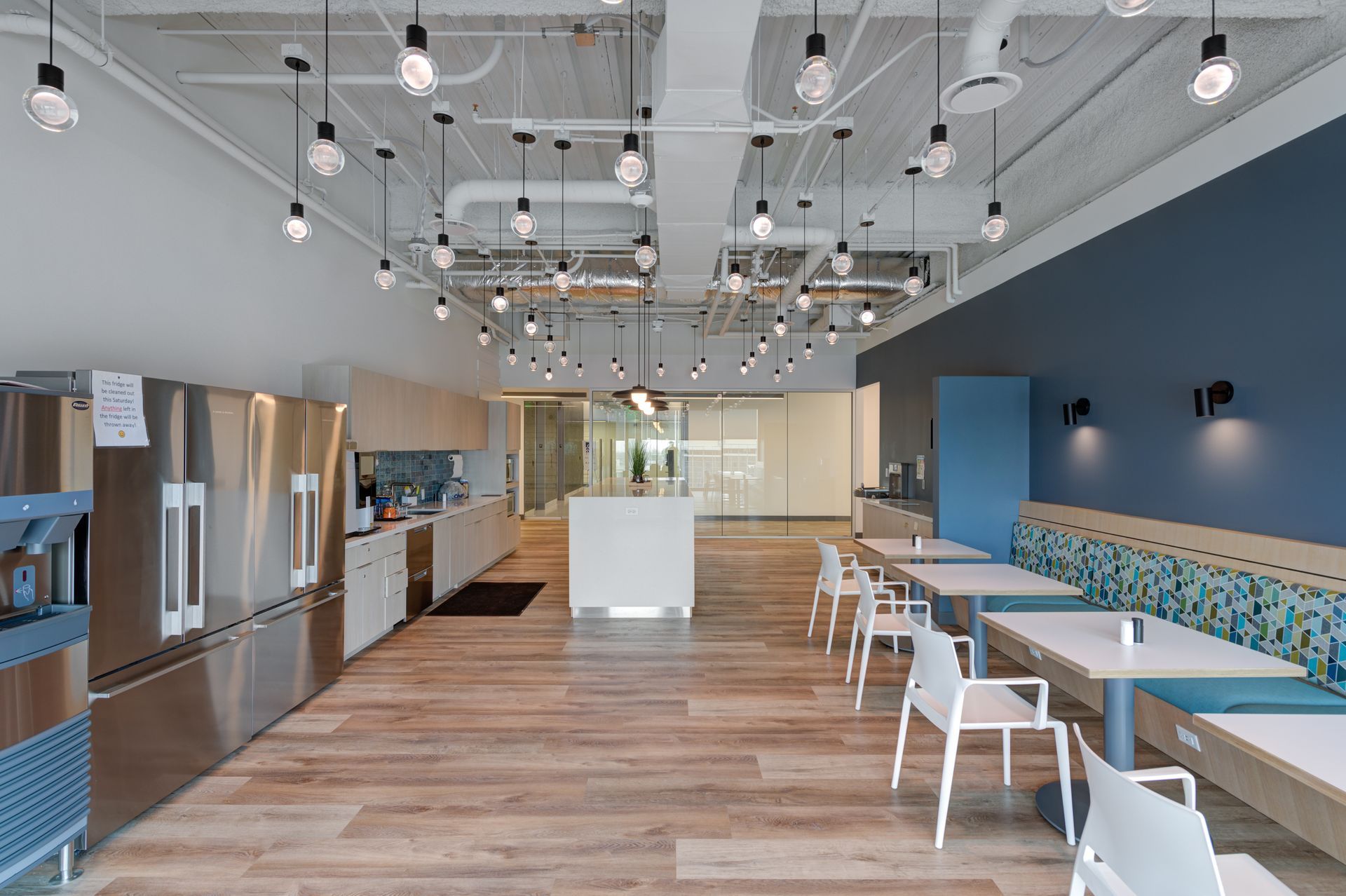
But if you want engaging, stroll through the lobby. The 15-foot ceilings there make for a spacious and inviting entryway to the 300,000-SF office. Soto mentioned the hospitality feel designed for the lobby—with high-end furniture, lofty ceilings, and views outdoors, the space is certainly engaging, but the material choices really bring the energy. Marble flooring from Afghanistan, marble wall tile from Vermont, floor to ceiling glass, and courtesan oak wood veneer from Texas all combine to form a first-rate lobby for the post-Covid office.
“Developers have really changed their opinion on what a lobby should be,” said Soto. Gone are the days of ceremonial places of sheer elegance meant to be hallways to a company’s actual office. In its place are comfortable, usable spaces that combine with the utility of the provided amenities.
The lobby is a feature piece, but the fully stocked fitness center can stand alongside as a top building amenity. It links to the outdoors via a glass curtain Panda Horizontal Sliding Wall—a hybrid feature sure to turn heads. Add those to the courtyard at ground level, terraces above, and even full conference rooms, and it seems fair to ask whether the amenities arms race real. “Absolutely,” said Tarro. In order to get people back to work, Tarro mentioned, “you have to check all of those boxes.”
Doing so is akin to adding stitches in the fabric; the fabric of this building is strong. At every level of the project, the project team is sure that they have built something that combines well with the city’s downtown evolution.
Tarro said that office space is poised for a rebound, with tenants unsure what their space needs look like in a post-Covid office environment. He and Patrinely Group are confident that future tenants will fall in love with higher floor plates, higher ceilings, and top-shelf amenities. He explained how “[Patrinely Group] wanted to check the boxes” for clients looking to make the move to Utah’s emerging office market.
“I’m confident that this building offers what tenants want today,” said Soto. It weaves together location, building quality, and amenities into one inviting campus. It will be a strength to Salt Lake as the downtown extends southward.
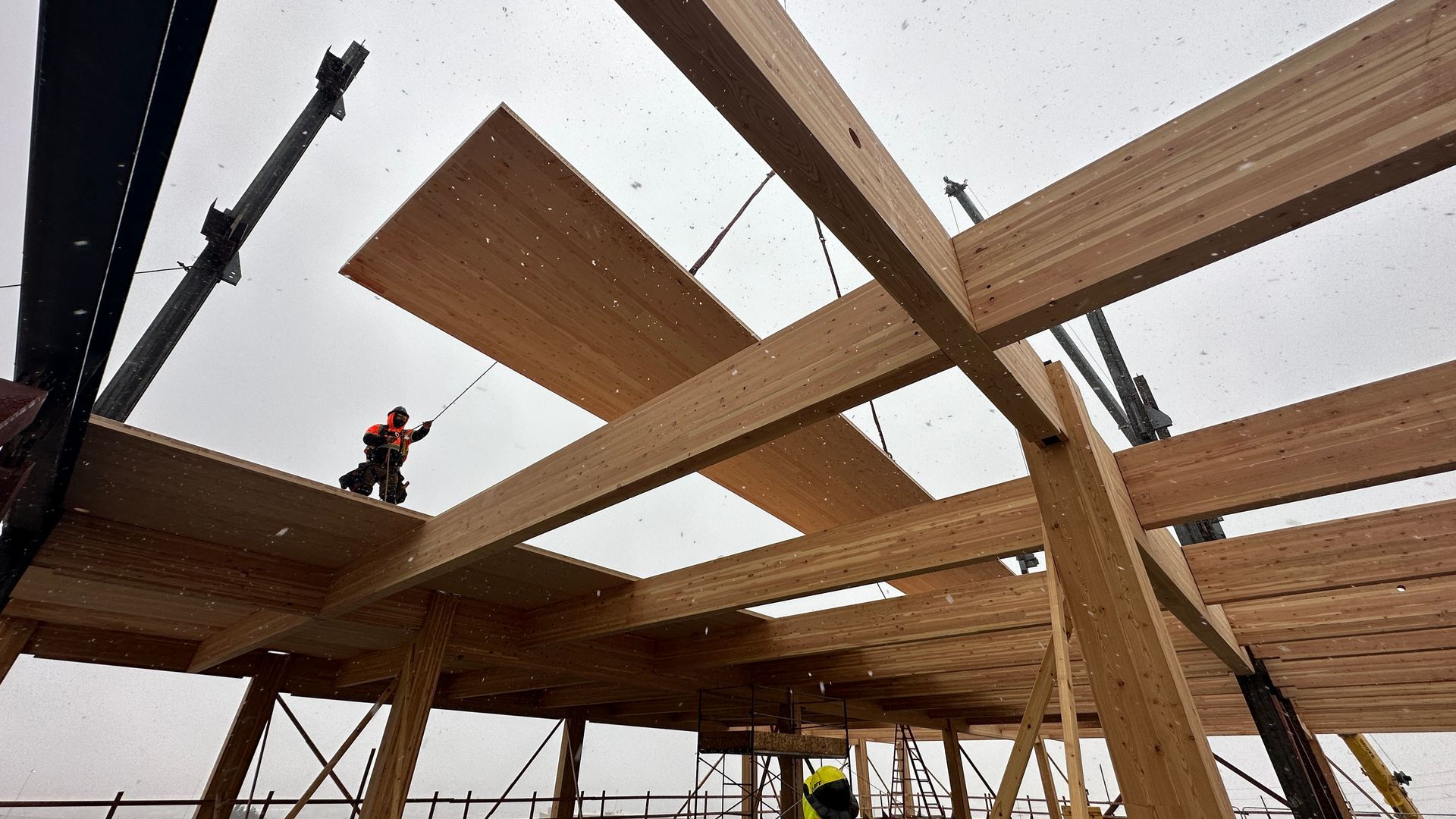

The continued spread of and improvements to BIM, new fuse plate technology, and the rise of mass timber are a few of the topics shaking up structural engineering in the Beehive State. Utah Construction + Design reached out to some Utah’s leading structural engineering firms to find out about current trends, technologies, and with five years of reflection, how are owners and designers looking at and learning from the 5.7 magnitude earthquake that shook the Wasatch Front in spring 2020. Jerod Johnson, Senior Principal at Reaveley Engineers, wrote a detailed retrospective of the event in 2023 and says researchers and engineers learned a few things from the quake from how different building types responded to insights into the geology of our region. “Research has revealed that the shape of the Wasatch Fault is different from what was previously believed. The Magna earthquake, initially thought to have occurred on a fault in the western part of the Salt Lake Valley, actually took place on the Wasatch Fault. The fault extends into the valley at a much shallower angle than expected, rather than descending steeply from the toe of the mountain. This new understanding of the fault's geometry has significant implications for seismic design and building codes. We anticipate changes to the spectral acceleration maps used in structural design. The lateral shaking observed during the 5.7 magnitude earthquake was much higher than expected,” says Johnson. “It highlighted the need for updated design practices that account for this amplification. These findings will influence future building codes and practices in Utah, ensuring that structures are better equipped to withstand such events.” But Chris Hofheins, a Senior Principal at BHB Structural, is concerned the wider public may not have learned enough from the event. “Most structural engineers thought the earthquake would be a wakeup call but to a large degree I think it had the opposite effect,” said Hofheins. “People looked around and felt like it wasn’t so bad and we’ll be alright if something bigger hits. We’ve seen a few owners who decided to increase the seismic safety of their buildings but we’re also seeing the opposite where I think some people are overconfident.” Blowing a Fuse Structural resilience, designing buildings that not only protect those inside during a seismic event but can be quickly reoccupied, continues to be of great interest to structural engineers. Replaceable fuses, or structural sections that can be sacrificed dissipating energy during a seismic event and then replaced, have continued to gain popularity with designers and improve the resilience of buildings. “This innovation represents a significant shift from traditional methods of enhancing ductility in earthquake design. Instead of merely adapting existing practices, replaceable fuses offer a new paradigm for building resilience,” said Dorian Adams, Senior principal and President with Reaveley Engineers. Adams said fuse technology like buckling restrained braces (BRBs) have been available and widely adopted for several decades. Newer proprietary systems like Durafuse, among others, for moment frames have been gaining popularity. “New technologies are emerging that offer exciting possibilities. One such innovation is the SpeedCore steel shear wall with a concrete core, which is included in the new AISC seismic provisions, the 2022 edition. This technology represents a significant advancement in seismic design,” said Adams. Replaceable fuse technology is also being employed with mass timber construction as interest in and use of the material around the world continues to grow. Jordan Terry, Principal at KPFF Consulting Engineers has designed structural systems for several mass timber and mass timber hybrid projects such as the ICCU Arena at the University of Idaho in Moscow and the recently completed Portland International Airport Terminal Core Redevelopment with its 400,000 sq ft mass Cross Laminated Timber (CLT) roof. He said there have been important advances recently in seismic systems for mass timber structures. “Typically, when you get a mass timber building over five stories you have to look at the seismic reinforcing and that is where you introduce something other than just timber. You might have a concrete core with the elevator shafts or use BRBs,” Terry said. “We had a client in Portland that absolutely wanted to use as much timber as possible. We helped develop a new system called a rocking CLT core wall. The base of the shear wall panels isn’t connected to the ground and it can rock back and forth but there are energy-dissipating sections or fuses, between the panels. They are very ductile. You swap them out and it’s as good as new.” David Dunn, CEO and principal at Dunn Associates, said the firm had utilized a rocking CLT shear panel in their design for a new all mass timber building currently under construction for the Zion National Park Discovery Center at the national park’s east entrance. Terry also said the firm was assisting researchers at the University of California San Diego in developing more all-timber lateral systems but noted like all materials, it should be used for its strengths. “CLT is really strong and stiff so you’d think it would be great for seismic reinforcement, but it is not very ductile,” he said. “We have a project in Spokane [Washington] where we used BRBs. We are letting the wood be stiff and strong like it wants to be and letting the BRBs deal with dissipation.” Hofheins noted mass timber research is going on here at the University of Utah as well. Dr. Chris Pantelides and the U of U’s Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering are developing a BRB encased in timber. Adams noted Dr. Pantelides’s project is not the only fuse research underway locally. “One such project involved a device placed in the middle of an X brace, with elastic braces and a fuse at the intersection of the diagonal braces. This device would compress and stretch, cycling through combined flexure and shear,” he said. “A University of Utah PhD candidate recently further enhanced this concept in his dissertation, adding curved plates of steel that cross one another and engage in tension only after reaching a certain threshold of displacement. This supplemental strength activates only when needed, providing a dual-level design solution that accommodates different magnitudes of earthquakes. The idea of replaceable fuses holds significant potential for the future of structural design. These innovations will become an integral part of performance-based seismic design, offering tailored solutions for varying seismic events. Simpson's Yield-Link connection is another example of this technology, although it is currently more suited for smaller applications.” Dunn said making buildings resilient and potentially reusable quickly after a seismic event not only has implications for safety but for sustainability as well. “Designing resilient structures is really an environmental consideration that is undervalued in my view,” said Dunn. “Code-based buildings will undergo massive deformations and damage after an earthquake. Sometimes small, incremental increases in first-costs can make huge differences in anticipated building performance, salvaging buildings that would otherwise be landfilled. That is a huge environmental impact, but not as buzzy as bike racks, low-water urinals, solar panels, etc.”
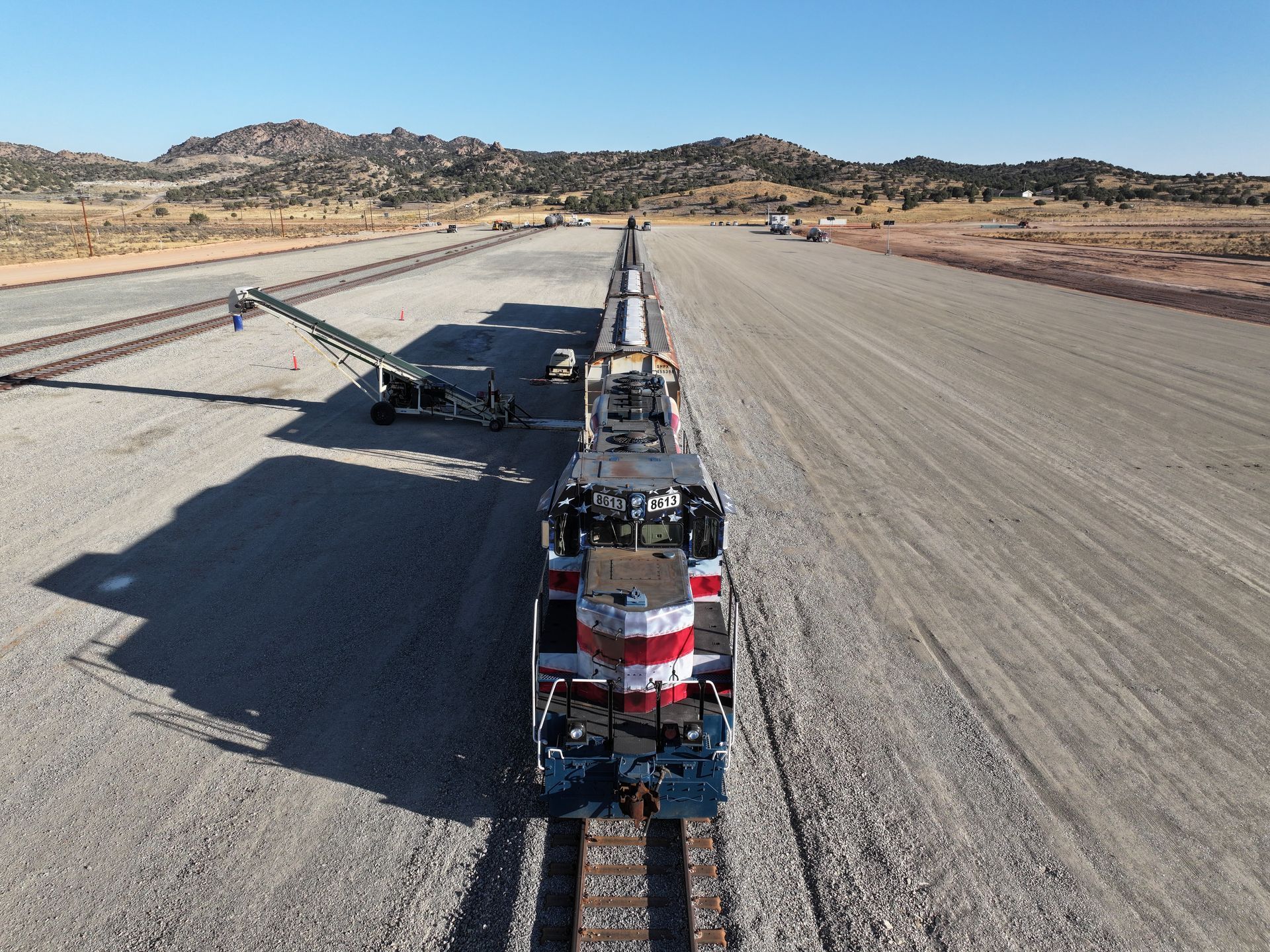

Ports? In landlocked Utah? Sure, the traditional idea of a port in Utah, with cargo ships, cruise liners, container cranes, dockworkers, barges—not to mention coastal water—is farfetched. But the Utah Inland Port Authority (UIPA) has broadened the meaning of a port since its formation in 2018. Even without a coast, UIPA has worked to strengthen rail, air, and road cargo infrastructure to turn Utah into a 21st century logistics hub and changing the economic trajectory of the Beehive State in the process. It’s been seven years of increased industrial development that has been a boon for the A/E/C community, but more importantly the logistics and manufacturing network to build for an ever-growing consumer demand. There have been plenty of detractors to UIPA, especially as it relates to ecological conservation. Ben Hart, Executive Director of UIPA, has heard it loud and clear as he sets the organization on a path to aid in development goals that benefit the entire state and the values Utahns hold dear. Origin Story + Coordinated Efforts UIPA was created to pioneer and implement strategic and sustainable logistics-backed economic solutions that enhance the lives of Utahns and establish Utah as a global industry connector. While UIPA began its journey overseeing 16,000 acres in the northwest portion of Salt Lake County, the Northwest Quadrant, it has grown in area and emphases since 2018. Today, UIPA is associated with 110,000 acres in 12 project areas across the state. Most importantly for the organization, Hart said, is how developments within UIPA project areas create high-paying jobs to strengthen Utah communities. Where regional logistics infrastructure does not exist, UIPA can make strategic investments to unlock regional economic growth. “Part of the [UIPA] charter is developing projects that provide economic strength for their entire region. Regional projects need regional infrastructure, which most importantly includes transportation infrastructure,” said Hart, detailing UIPA tools to build out transportation infrastructure intended “to help grow the entire regional economy. Hart said that UIPA has grown its overall area scope to help meet statewide initiatives from current Governor Spencer Cox and regional initiatives from municipal leaders around the Beehive State. Speaking specifically of many of Utah’s rural counties, “There is more commerce going on in those areas than what people recognize,” Hart said, “and you still have a really good workforce in those areas as well.” Municipalities and counties of all levels (see project area map) have been willing to go through a four-step process to access UIPA capabilities in route to industrial development and the high-wage jobs that come with it.
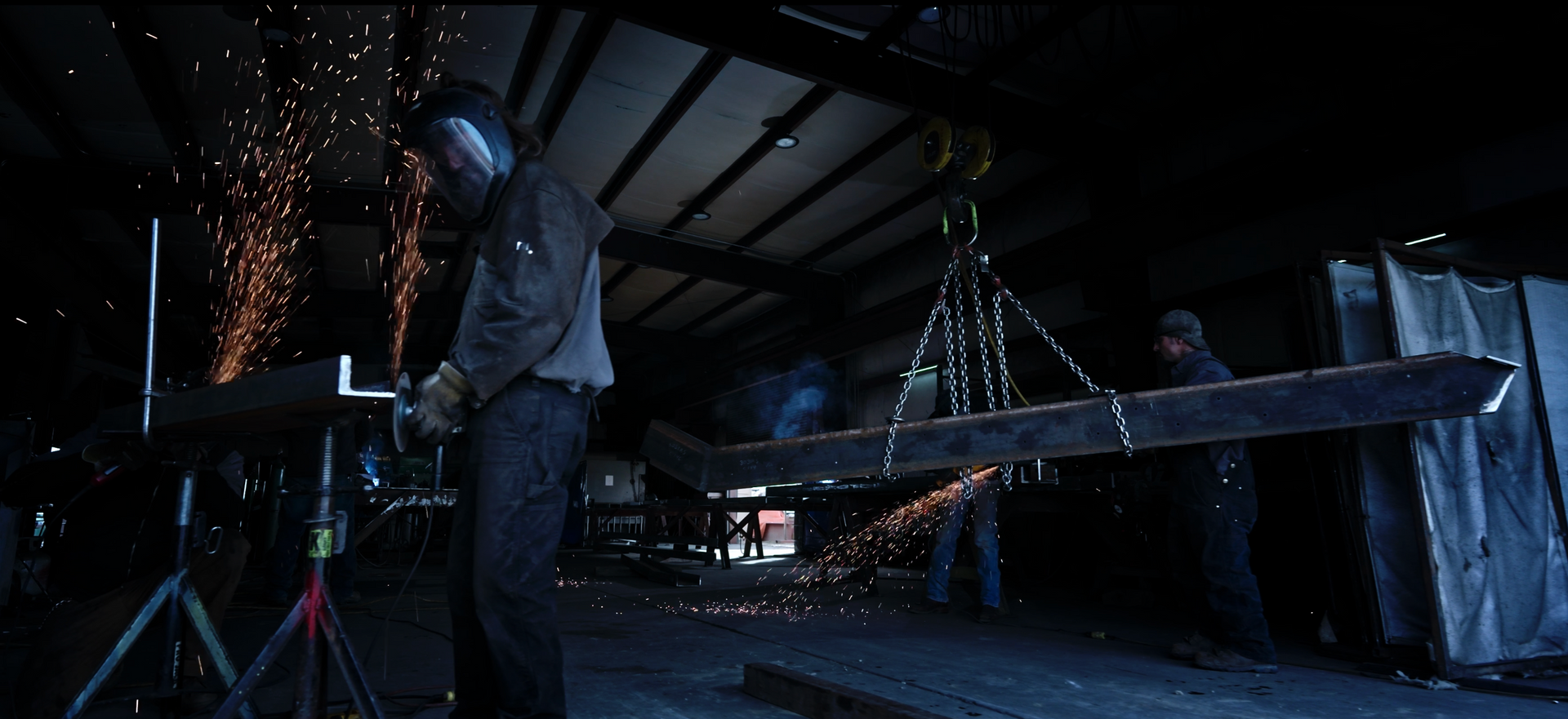

Tariff talk is loud. But don’t let that be the only thing that garners attention in steel fabrication trends. Leaders in this field said that they continue to innovate and build up their spot within the industry to ensure steel continues to be utilized in projects across the Beehive State. Tariffs Add Volatility On March 12th, 2025 the Trump administration announced 25% tariffs on all steel and aluminum imports. With over 25% of steel imported, according to the US Dept. of Commerce, steel procurement is set to get even pricier. Matt Blaser, President of Price-based Intermark Steel, sees plenty of similarities with tariff policy and the pandemic effects on the supply chain. Much as supply chains needed reconfiguring during the pandemic, “The overarching goal [of tariffs] is to bring manufacturing back into the United States,” said Blaser. “Where we’re not dependent on a global supply chain.” It’s worked as intended before, when 2018 tariffs (25% on steel imports) helped increase domestic steel production by 6 million tons from 2017-2019. For Richard Wood, President of West Jordan-based Rightway Steel, the expected increase in domestic steel production, “It’s just getting started. Many new companies have plans to build steel producing plants in the US.” These incoming ‘minimills’ are bringing faster throughput in a smaller area via a much more efficient steelmaking process. According to a 2020 U.S. Environmental Protection Agency report, over half of the national steel output was produced in minimills. These mills use an electric arc furnace (EAF) to melt and refine steel scrap by passing an electric current from the electrodes through the materials to melt it at a scorching 3,000 degrees. It’s making blast furnaces and “rust belt” technology a thing of the past. But on-shoring production has still been a tough pill to swallow for fabricators as steel prices surge. “As of April 1st, steel material prices have increased upwards of 25%,” said Wood. “We’re unsure if or when the tariffs will be reduced.” Even as tariffs escalate, fabricators like Rightway Steel have sought a way forward even as Wood has seen demand and project starts slow down. Rightway has pivoted with new pricing, reduced quote hold times, and internal efficiencies to stay competitive. As developments in EAF take a greater share of steel production market toward stability—and hopefully lower prices—those internal efficiencies Wood mentioned will shape the future of steel fabrication. Innovating Internally “In any steel fabrication, or any type of production, there is a four letter word that makes all the difference: flow,” said Tyler Oliver, President of Centerville-based Fineline Steel Fabrication. Limiting the amount of movement required from the fabrication team in the shop is one internal efficiency keeping costs low. Inside Fineline’s shop, TV screens and tablets keep the team in the shop fully aware of what’s going on—and keep everyone in flow. Touring through the firm’s Centerville shop, one quickly notices how long the building is. Think arena football field, but five of them end to end to reach 1,000 feet long. If Fineline could have a facility twice as long and half as wide, Oliver said, it would help that flow even better. Oliver claimed that Fineline;s facility houses “One of the most state-of-the-art fabricators in the world.” Fineline’s Voortman Steel Fabricator has been a key part of the firm’s innovative flair. The fully-automated welding system starts with the VACAM system to determine the feasibility of assemblies, production times, etc—particularly helpful when determining the amount of automation required in the welding process. From there the magnetic handling robot grabs the steel pieces fed by the Fineline team, rotates the steel, and welds steel members in the right place. Rightway Steel has looked for similar internal efficiencies, with Wood saying the firm is improving year over year with new equipment and processes to improve quality, speed, and safety. “There’s always room for improvement,” he said before mentioning how it will be incumbent on fabricators to find or train workers capable of learning the ropes as the company invests in more robotic welding, improved machinery, and emerging technologies like wearable exoskeletons to keep production humming. Technological Infusion With lead times getting shorter for many of these projects, Oliver said, “[Owners] need their parts and members bigger, better, and faster. This is why we have innovated and are constantly working on adding automation.” Technological innovation reigns supreme. Construction software Stalwarts like Procore and Building Connected are combining with emerging technologies that incorporate in-field scanning from team members to improve accuracy. “We have also seen improvements in modeling and steel shop and erection drawings through Advanced Steel and Tekla,” said Wood. As modeling has improved, so has the final product created by fabricators. Blaser echoed Oliver’s comments on speed to delivery and Wood’s thoughts on digital collaboration, saying that the ability to fabricate from a digital file has been catalytic in today’s high-speed construction market. Blaser also reiterated points from the other fabricators regarding internal systems. Having a CNC machine isn’t enough—it’s the bare minimum. Instead, working in a “Henry Ford-esque” assembly line makes all the difference today, especially when combined with digital innovations and steel detailing software. But the future is one where those systems are bolstered by AI. “Larger companies will have machines interconnected via AI,” said Blaser. With enough capital to invest in interconnected machinery that needs less human help, AI adaptation within steel fabrication will “Consolidate the market and probably push smaller shops to the wayside.” For Oliver, “AI is the top of our list as it is with everyone else,” namely allowing the team to spend their time processing material for fabrication. “There are some major advancements with AI and how we can final QC some of our members.” While AI grows in importance on the shop floor, Wood said his teams have utilized AI as much as possible in the office for great efficiency in take-offs, proposals, RFI support, and meeting information.
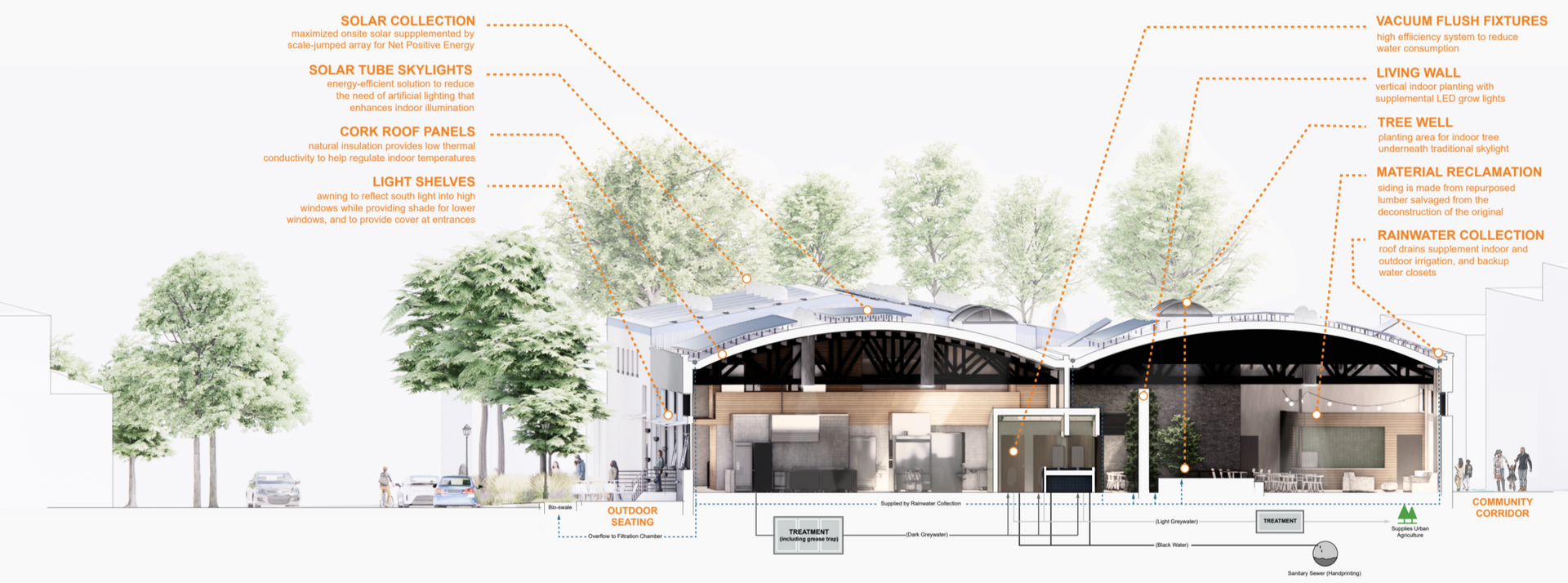
“Our thinking needs to be challenged in our culture.” The words from Bill Reed came during his keynote address at the Intermountain Sustainability Summit held at Weber State University in late March. And the strength of his advocacy for a sea change in how our culture thinks about everything—especially sustainability—only continued. “There is no such thing as a sustainable building,” said Reed, Principal of Regenesis, a regenerative design and education organization based in Santa Fe, New Mexico. Reed spoke from experience. He is a founding board member of the US Green Building Council (USGBC) and Co-Founder of the LEED Green Building Rating System. For him and many others, LEED won’t be the answer to the problems posed by the built environment. “LEED came along to tell us we could do things better,” he said. “But sustainability is a slower way to die.” “Places are living organisms,” he said. Everyone involved in development must realize, “Your project is not ‘The Project,’ but is part of a living system,” where the development in question is part of an expansive web of community priorities. “We have to make common ground in these communities,” he said, where alignment results in a project that fits within multiple contexts. Reed’s words were strong, and he challenged sustainability experts to find ways to create a regenerative built environment and all of its positive outcomes. UC+D looked to continue those thoughts and reached out to multiple design experts to see how to challenge our collective thinking and steer us to a sustainable future for the built environment. Value Alignment from the Start When Garth Shaw approaches a project, he starts with a fundamental question: "What does our client want and need, and what sustainable design strategies will help them get there?" Shaw, Principal and Director of Sustainability at Salt Lake-based GSBS Architects, said the goal is a high-performance, sustainable design that promotes, rather than dictates, client objectives. Efficient, resilient, and healthy buildings emerge from this process. “There is so much momentum in the industry to move faster and cheaper,” Shaw explained. Everyone in the A/E/C industry values efficiency, and private developers and owners are no exception. However, they also prioritize predictability. Even when a project starts with ambitious sustainability goals, compressed schedules and cost pressures can lead teams back to old methods. "It worked last time!” becomes the enemy of progress. Shaw argued that the industry must create space for innovation. "We need time to drive deep value into buildings that precisely meet client needs while protecting—and even enhancing—environmental performance." Overcoming this challenge begins with aligning values. “If you can tie people’s values into a practical approach to sustainability, that’s the magic,” Shaw said. He encourages his team to lead sustainability conversations without defaulting to LEED certification. Instead, successful sustainability strategies require tools tailored to each project. This kind of value-driven approach has broad appeal, transcending political divides. Shaw noted that leaders across the political spectrum recognize the importance of sustainability through air quality and water conservation efforts. Depoliticizing environmental stewardship is key—it’s not just a policy issue but a human issue that affects everyone. Government incentives, like the Inflation Reduction Act, have helped make sustainability more attractive to owners. The IRA provides substantial discounts for projects implementing energy-efficient systems, such as Utah’s on-site ground-source thermal exchange systems, which can now receive up to a 50% discount. When cost savings are clear and measurable, sustainability becomes an easier sell. Beyond energy systems, sustainable construction also hinges on material choices. "Manufacturers and contractors aren’t used to tracking carbon impacts," Shaw noted, but forward-thinking industry leaders continue pushing for better transparency. Tools from organizations like the Carbon Leadership Forum help architects, builders, and owners visualize the carbon footprint of materials, empowering them to make informed decisions. For the A/E/C industry, staying ahead requires continuous learning—keeping up with evolving grants, materials, supply chains, and building systems. Shaw concluded, “Change is required, and that change will ultimately benefit our clients. It may take more time, but the result is a high-value project—for people and the environment.”
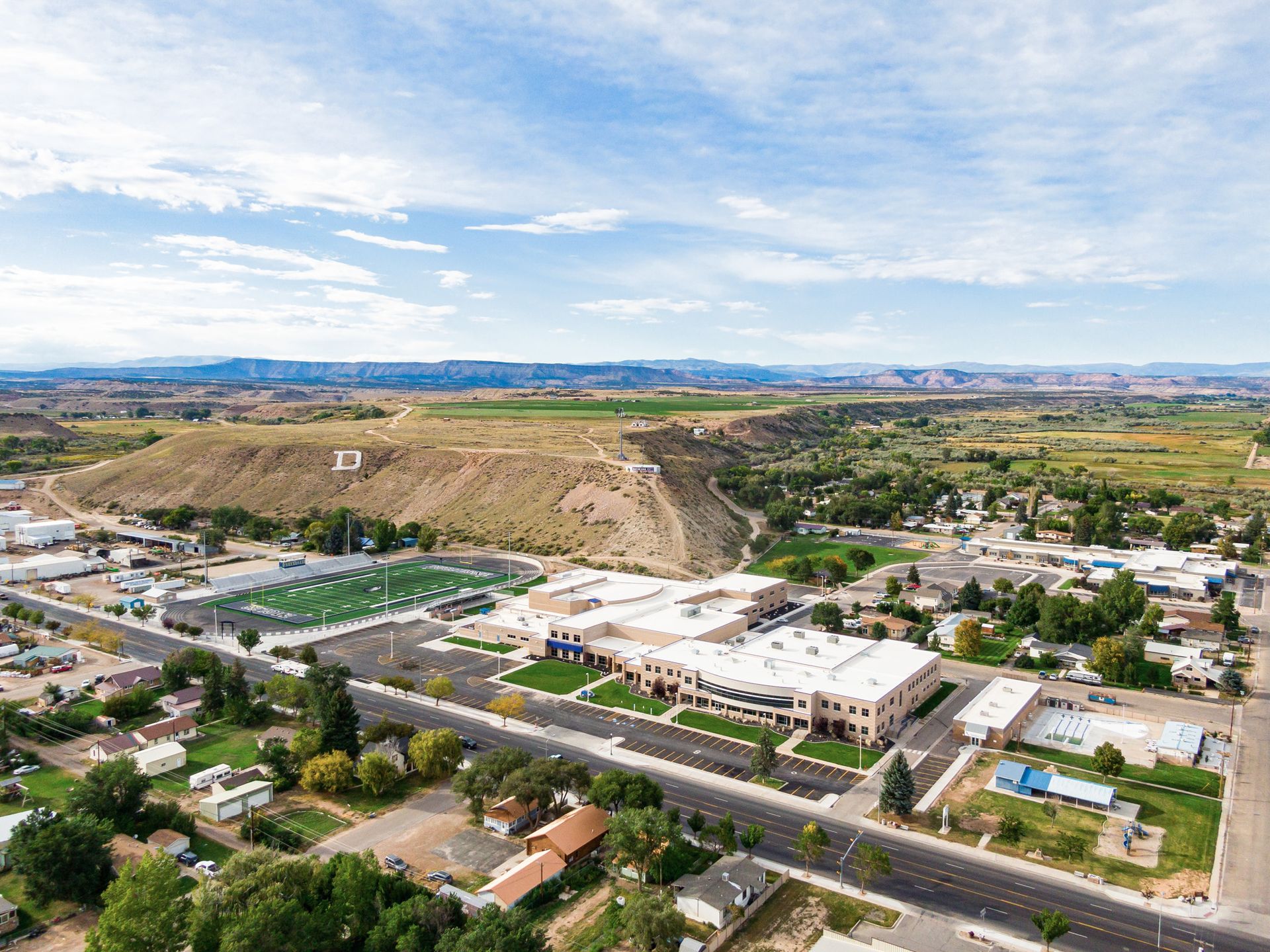

The recently completed Duchesne High School (DHS) renovation is a textbook case of the old wedding adage: “Something old, something new, something borrowed, something blue.” Fittingly, the project resulted in an elegant marriage of design, construction, and community spirit. The old and new are carefully blended, with brand-new buildings and modernized spaces standing alongside preserved sections of renovations past. And to tie it all together? The commons area, a brand-new roof, and other key highlights are bathed in Duchesne’s signature blue color. Naturally, like any good marriage, this $62.9 million rebuild required commitment, collaboration, and a little bit of patience. Architects, builders, and school district officials worked hand in hand to ensure that the old and new came together in harmony—honoring the school’s legacy while preparing it for the future. “We strived to make a space that brings pride to the students, staff, and the community,” said Wes Christensen, Principal Architect at KMA Architects, the Spanish Fork firm that designed the rebuild. “Our approach and design philosophy were heavily influenced by the desire to create a cohesive and efficient addition that would seamlessly blend with the existing portions to remain. We feel that we were able to accomplish this successfully, working together as a design team, including our consulting engineers, the school district, school administration, and Westland Construction.” Save the Date The Duchesne High School rebuild has been on the drawing board for nearly seven years and in the construction phase for 33 months. KMA started the design process in 2018, but the project was put on hold by the Duchesne County School District due to COVID and faced additional delays because of supply chain issues and long lead times for equipment. Westland Construction of Orem eventually earned the CM/GC bid and broke ground in June 2022. The high school remained open during the course of construction, creating the need for innovative and meticulous planning to ensure safety while working around normal school activity. “The new addition at the school was built where there was a field, parking lot, old basketball gym, and shop classrooms,” said Aaron Kirkham, Project Manager at Westland Construction. “The remodel and construction in the existing school areas were done during the school summer breaks.” When school was in session, temporary construction fencing and gates around active working areas served to keep students safe, Kirkham said. Construction delineation kept workers and equipment separated from students and staff. According to Michael Weldon, Building and Grounds Supervisor with the Duchesne County School District (DCSD), the detached gym and locker rooms were built in 1965, the auditorium and shops built in 1974, and a newer building added to campus in 2005. “The parts of the school that were demolished did not meet current building codes,” Weldon said. “The original auditorium was extremely small and the shops were also small. You had to go outside and through a parking lot to get to the second gym. The new build project incorporated the shops, an auditorium, and gym attached to the 2005 building so that they feel and look like they were built at the same time.” Bridging the old and new construction is always a unique factor that is different for any remodel and addition project, Christensen said. “These previous additions were designed by another architect, so that also creates a challenge to overcome in blending styles and design choices.” One of the most significant hurdles revolved around the central placement of the auditorium within the new school structure. While beneficial in creating a focal point for the building, the new auditorium posed myriad logistical challenges during construction. According to Kirkham, a 28,000-pound steel beam needed to be placed to support the structure’s masonry walls, which were 35 feet tall. The beam placement required a 550-ton crane, which had to be strategically positioned where the future gym would be constructed. “As a result, we had to delay the construction of the masonry walls in the new gymnasium until the beam was in place,” Kirkham said. “This sequencing created a very compressed and demanding schedule to ensure the new basketball gym was completed in time for the start of the school year in August 2024.” Despite those constraints, Kirkham said, construction on the gym’s masonry walls and concrete slab began in January of 2024 and was completed within seven months.
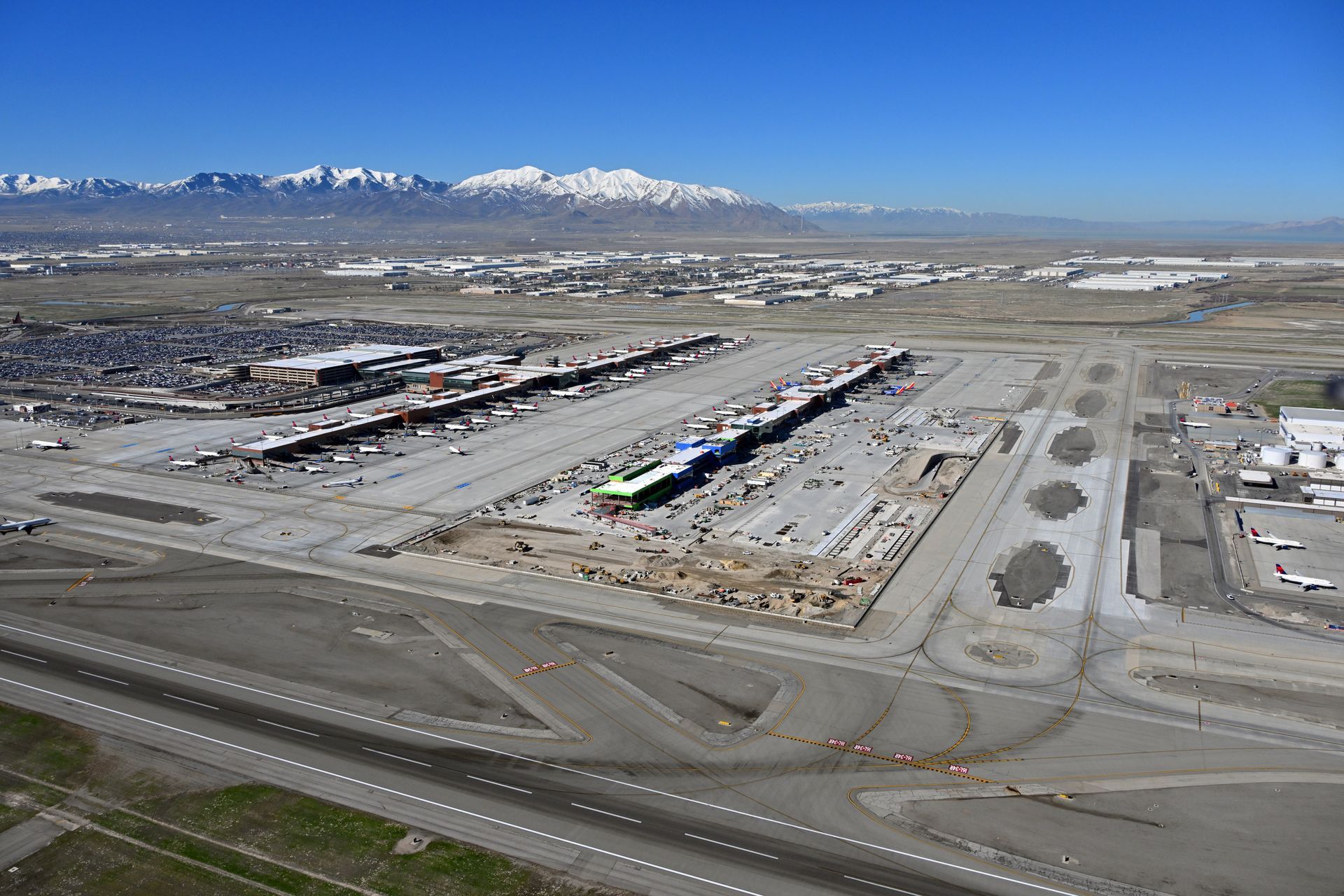

The historic Salt Lake City Airport Redevelopment (the New SLC) project continues to roll on into its fourth—and final—phase, with a targeted finish in October 2026 and final delivery of 16 new gates in Concourse B that will allow it to serve 34 million passengers annually. At a whopping $5.135 billion, the New SLC marks the single largest project in Utah's history, with the Phase I grand opening in September 2020 the first of many project milestones. The New SLC also sports the distinction of being the first new hub airport in the U.S. built in the 21st century, making it one of the most modern, technologically advanced, and aesthetically pleasing airports in the world. Last October, the $458 million Phase III was delivered by the Holder/Big-D Construction Joint Venture (HDJV) team, highlighted by the dynamic new 1,175-foot Central Tunnel—dubbed the "River Tunnel" for its mesmerizing blue ceiling art installation that depicts a flowing river—along with the Concourse B Plaza. The new plaza features an extension of the popular canyon motif with new art installations and the remarkable preservation of the former airport’s iconic "World Map" terrazzo floor section originally installed in 1960. Mike Williams, Program Director for the New SLC, expressed his excitement at the completion of Phase III, saying it's the most significant project milestone since Phase I opened in 2020. "This is really what I call the second transformation of the airport. The first was when we opened Phase I in the fall of 2020," said Williams, the veritable maestro of this Herculean, once-in-a-lifetime project. “[Phase III] is the one that ties it all together and makes it function as one cohesive airport." Williams said it's been remarkable to see how this project has morphed since it was announced more than a dozen years ago. At that time, the scope called for constructing just a new Concourse A and landside facilities. When the pandemic hit in March 2020, a mere six months before the scheduled grand opening of Phase I, SLC Airport officials pivoted with the original program and called for Concourse B to be built as well, essentially adding Phase III and Phase IV and nearly doubling the program budget to exceed $5 billion. Having the same general contractor team (HDJV) and design team, led by San Francisco-based HOK, on all four phases allowed a more seamless expansion since the goal of building Concourse B was to have it look and function virtually the same as Concourse A. Bill Wyatt, Executive Director of Airports for Salt Lake City, has been involved since 2017 and praised all parties involved for the successful completion of three major phases thus far, and for continually trying to improve the construction process from phase to phase. "During Phase I, we had this constant barrage of issues," said Wyatt. "I'd go on these construction walks with Mike [Williams], and someone from [HDJV], and it was a constant series of decisions that had to be made. We fixed all of those little things so that almost none of those issues were in Phase III and Phase IV. It's kind of like rinse and repeat—they're going on 10 years of building gates, and they have it pretty well down by now." Wyatt agreed with Williams that Phase III is the essential functional piece tying the entire project together, with the Central Tunnel being a vital connector between the two new concourses. The Central Tunnel makes a strong statement with its unique aesthetics and general stress-free vibe—highlighted by a carefully curated music playlist designed to help visitors decompress from the stresses of traveling on their journey to Concourse B. "In some ways, other than the [Phase I] grand opening itself in 2020, the opening of Phase III is the most significant," said Wyatt. "It makes the airport flow and function so much more effectively. Prior to this, people had a hard time understanding how it was going to come together—the Central Tunnel and Plaza of Concourse B really bring that together. We're very happy with the end result, the art [...] everything about it is terrific." "There has been a ton of excitement seeing the public's reaction to the Central Tunnel opening," added Jordan Cammack, Construction Director for the past two years for HDJV, and a former Project Manager and Senior Project Manager who has been on the job since construction began in July 2014. He praised the cohesiveness of the design and construction teams over the past 11 years and the ability to make changes without disrupting the schedule or budget. "It's been impressive to see how the architect and design teams came together and worked with us throughout the project," Cammack added. "It's been a great job—it's been like a family out here with all our team members, owner reps, and architects. We've seen families grow up. It's a pleasure to come to work with such great people for an extended period of time."
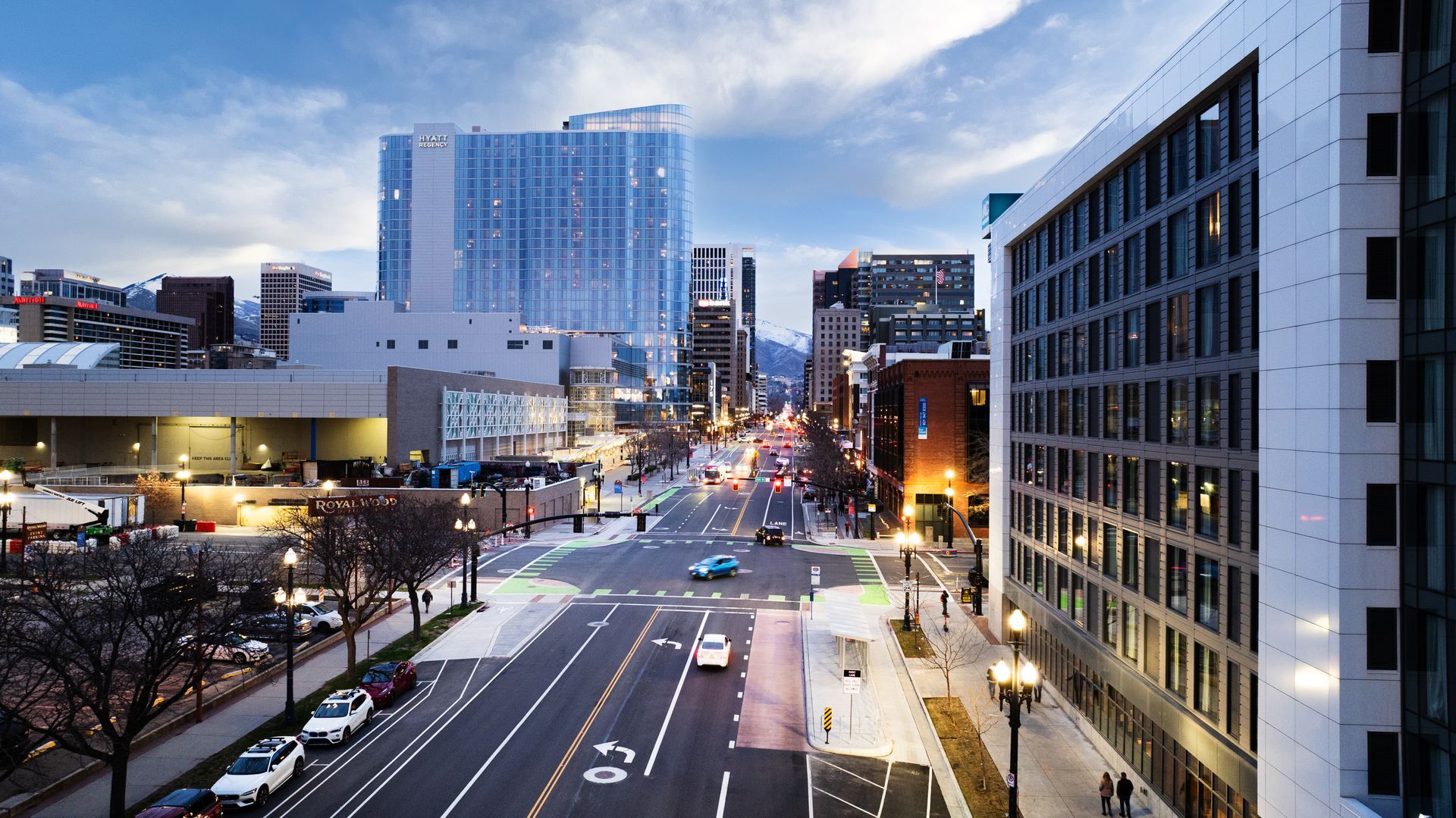

“What does this corridor want to be when it grows up?” The question posed by Kyle Cook was the impetus for the 200 South Reconstruction project. It helped usher in a new era for Salt Lake City’s bus corridor with the tagline: “200 South—A Place of Motion” Cook, PE and Transportation Engineer for Salt Lake City, said 200 South was discussed years before design and construction commenced, namely from the capital city’s 2017 Transit Master Plan. After evaluating 15 corridors, 200 South was deemed the most important. “A strategic corridor,” said Cook of the area from Salt Lake Central Station to the University of Utah. Working in tandem with UTA and multiple Salt Lake City departments, the design would condense the five lanes of the old street into three passenger vehicle lanes, two dedicated bus lanes, and two bike lanes. It would create a street that matches the urban character of the area, one that is much safer and better equipped to handle the multimodal traffic on 200 South. Building for Community Needs As the Salt Lake City team went from master plan to design in the early days of the pandemic, they turned to online workshops, surveys, and virtual town halls on Facebook Live to get feedback on what folks hoped to see from a reconstructed 200 South along an area between 900 East and 400 West. “At the time, that was pretty novel for us,” Cook said of that public involvement work from the city and AECOM consultants, who served as project prime. “But I think we got very good at it.” They took in nearly 1,000 survey responses plus online event insights to determine the street needed to accommodate not just buses and passenger vehicles, but pedestrians, cyclists, and the array of businesses housed along the corridor. Reconstruction of 200 South was a two-phase project, where Phase 1 would cover 900 East to 200 East, and Phase 2 would reconstruct the far busier part of the project between 200 East and 400 West. Working with the Business Community Road construction is the bane of many and grows more challenging for a project team attempting to accommodate businesses and travelers while building in an urban environment. “It’s as downtown as it gets,” said Brett Kearns of the project scope. “The amount of vehicular or foot traffic passing through, and knowing you have to re-do the entire street, remove curb, gutter, and flatwork—it’s a huge concern.” Kearns, Project Manager/Estimator for Acme Construction, said they worked hand in hand with Salt Lake City and the public engagement team at Avenue Consultants to address business needs as construction continued between each phase. “In order for 200 South to succeed, we have to have good contact within our team and good contact with businesses,” said Kearns. “The first thing we did was canvas on the corridor,” said Stacee Adams, Public Involvement Manager from Avenue Consultants, who managed public involvement from the end of design through project completion. Adams said the team “went business to business” to show them what would go in place, infrastructure amenities, and what to expect in construction. Beyond the initial meet-and-greet, the team hosted workshops at Gallivan Plaza, took daily phone calls, and met with businesses monthly to keep them in the know. They also provided information to event attendees at places like the Greek Fest (300 West) and the Salt Palace (West Temple - 200 West) to keep visitors aware of construction impacts. Working Around the Barriers Acme’s experience on other Salt Lake City projects, notably the successful 900 South Corridor reconstruction, gave the city confidence that the Acme team would build community trust in each phase. That proved especially critical with the Capitol Theatre (50 West). Uneven grades surrounding the building posed one challenge while accommodating Capitol Theatre’s busy schedule posed another. Beyond venue patrons, “[Capitol Theatre] has load-in for their stage equipment, performers and costuming coming in, plus students coming in on school days for plays,” said Adams of the complicated logistics plan required. “We found out the best time for them was for construction to work from the beginning of July to August 15th,” said Kearns, who noted the atypical nature of the project required a level of dedication matched by the construction team across both phases. Kearns especially praised Acme Superintendent Herman Sword, who coordinated across the project’s two phases and ongoing construction projects nearby to ensure good outcomes for everyone. The Acme team installed plenty of asphalt and concrete to give the road and sidewalk new life around a bevy of ongoing work. Enbridge Gas installed their pipeline along the same corridor, Royal Wood Plaza (230 West) underwent demolition, and construction progressed on Zephyr Lofts (370 West) and Astra Tower (State Street).

Despite some minor economic headwinds, Utah is poised for another solid, if semi-unspectacular, year of construction and real estate development, according to top economists locally and nationally. Indeed, 2025 is shaping up to be much like 2024, a year where firms across the A/E/C spectrum completed dozens of life-enhancing, community-uplifting projects across every major building sector—in other words, a lot of projects were built outside of the still churning multi-family market. These firms thrived for the most part, posting positive revenue growth and maintaining momentum in the face of the usual challenges of shallow labor pools and volatile material costs. Utah continues to rank among the top states nationally on key economic drivers such as population growth, construction employment, a pro-business climate, and a legislative body that continues to be bullish on funding higher education and transportation projects. Prospects are good with a can-do mentality among developers, municipalities, and the firms designing and building the jobs. "Utah will continue to have above average growth and is in great position to continue its great track record with a growing population, and a strong economy and construction market," said Ken Simonson, Chief Economist for the Associated General Contractors of America (AGCA) in Washington, D.C. "Utah has been on a steady, strong upward path with 27% growth in construction employment—three times the national average of 9%—since 2020." Simonson said Utah's construction employment growth doubled last year, up 6%, which is twice the U.S. average. Growth would be even stronger, he added, if contractors could find workers, particularly skilled tradesmen. Simonson said a survey of 1,500 firms nationally stated 94% had openings for craft workers. "It's hard to fill (skilled) positions, more difficult than last year," he added. Utah's consistent population growth—the Beehive State ranked fourth according to the U.S. Census from 2023-24 with 1.8% growth (3.44 million to 3.50 million)—is a driver of demand for so many types of construction, as well as a course of construction labor. Simonson said the state has been more welcoming of immigrants, an important source of labor for contractors across the board. Utahns also have a reputation for being well-educated coupled with a strong work ethic and drive to succeed, making the state an attractive place for new businesses looking to expand. Developers Waiting Out Interest Rates; Hope for a Drop in '25 The Fed kept interest rates where they are in January—a decision not popular with many real estate developers simply itching to invest capital and have projects waiting to cut loose the minute rates become more favorable. That pent-up demand could heat up the market if rates drop by even half a point, particularly in the multi-family arena. Simonson said multi-family was down nationally 8% from September 2023-24, with Utah seeing an equivalent slowdown, despite a huge amount of inventory that hit the market in 2024, including attractive high-end downtown properties like Camber, The Worthington, and Astra Tower, and many others along the greater Wasatch Front. "Reductions in the [Fed]’s short-term interest rate target will make financing a bit less expensive but developers still can't get loans or want to proceed if rents aren't high enough to cover the financing and construction costs, including time to complete if there are extended delivery times for electrical equipment such as transformers and switchgear," Simonson added. "Utah isn't immune from these challenges, but if the underlying population growth will be supportive of rent increases, that may bring back multi-family construction sooner than in areas that aren't growing as fast, or at all." Spendlove Keynote at 2025 NAIOP Symposium Senior Economist for Zions Bank, Robert Spendlove, said Utah is well-positioned to maintain solid economic activity, with factors of low unemployment (hovering around 4%), solid wage growth (3.9% in December), and more than a quarter million jobs added at the end of last year. "Utah had unexpected, continued strength in the labor market," said Spendlove at NAIOP Utah's 2025 Symposium in January. "If we could pause the economy and stay where we're at now, we'd be in a perfect position." Consumer inflation, he said, remains sticky at nearly 3%, with the Fed targeting 2% before they can lower interest rates. "Until it's at 2%, they can't claim victory," he said. Overall, consumer prices are up a whopping 22% since 2020. "It's a struggle for people—those prices are never going back down. Inflation is just adding to those price increases. [Fed Chair Jerome] Powell said they will not make the same mistake as the 70s; they will not cut rates until inflation is down." In addition to strong 1.65% [WHAT TYPE OF] growth and 1.8% employment growth, Utah rebounded quickly from the pandemic. "That shows the strength of Utah's economy and labor market," said Spendlove. He added that Utah's GDP was up 4.6%, indicating the strongest economic growth in the U.S., with consumer sentiment improving and greater small business optimism. Utah Maintains Steady Growth, Says Eskic The Beehive State's remarkably consistent and steady growth remains a major reason why its economic outlook remains rosy, said Dejan Eskic, Senior Research Fellow at the Kem C. Gardner Policy Institute at the University of Utah. "Utah's population growth has never dropped below zero since 1950—we're still increasing with net migration," said Eskic at an event hosted by the Intermountain Chapter of the American Concrete Institute in January, with growth slowing by only .08 to 1.65% "There is so much demand in our economy that even in a down year for housing, construction employment is up 6.2%," he said. "The American household, on average, has never looked better on paper when looking at financial stability," with 70% of household debt tied to mortgages. Living in Utah is still expensive, even though the state is now listed as the 10th most expensive state to live in, down from 8th. "It doesn't mean Utah is more affordable, other states are just more expensive." The housing crisis will remain among the biggest challenges, both with affordable housing and overall number of units that need to be built. Governor Spencer Cox has made his intentions known that communities need to prioritize ways to address all housing issues, with a desire to see tens of thousands of single family homes built in the next decade. Way easier said than done, simply because developers cannot be expected to be altruistic when market conditions are competitive and profit margins potentially volatile and risky. He expects rents to increase once absorption is reached. Other items of note: —Consumer Price Index dipped to 2.6%, where it is expected to stay. —Expect growth in wages and employment. —Commercial construction will be primarily flat, similar to the last two years. —Office is flat, medical and industrial markets will continue to grow; industrial may be dictated by international trade. —Utah expects to add 500,000 people in the next decade, and will need a jaw-dropping 275,000 more housing units in that time, primarily along the Wasatch Front. "We need to change the dialogue if we're going to solve the housing crisis," said Eskic. "Currently, 92% of renters are priced out of the market. Construction must be optimized."
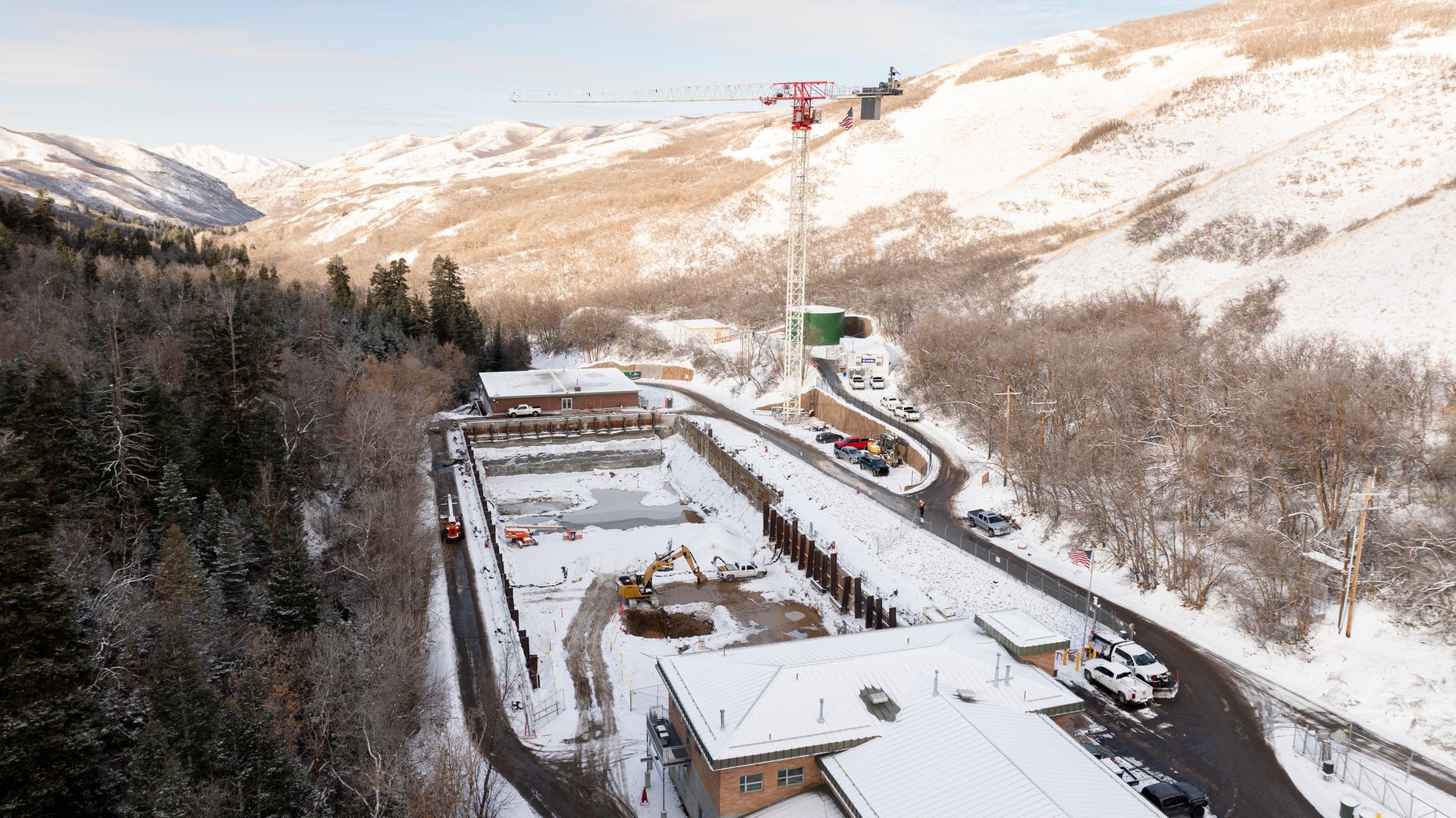

July 23rd, 1847 was a pivotal day for the pioneers. Records from the time detailed how the advance party trekking into the Salt Lake Valley built a dam to convey water from City Creek to freshly plowed land. Years later, the city hired civil and hydraulic engineer Herman Schussler to design a system to bring water through laminated wood pipes to 20,000 Salt Lake City residents while preparing for future growth. Schussler said, in a presentation to Brigham Young in 1872, “I propose to construct the pipe system of the City of such dimensions as to be capable of supplying five million gallons per diem.” While those original pipes couldn’t make it to year two, the design was in place for cast iron pipes to go in their place in 1876. The 37 carloads of cast iron pipe, plumbing tools, water gates, and more came from multiple suppliers from eastern US industrial hubs of St. Louis, Boston, and Louisville, KY. Those collaborative efforts brought modern waterworks “in our lovely Deseret,” collecting water from 19.2 square miles of watershed that feeds the 14.5-mile-long City Creek stream. Modernity Fast forward nearly 150 years, past chlorination that arrived in the 1920s, past the first water treatment facility constructed in Utah, the City Creek Water Treatment Plant in 1953, past filter installation in 1966, and past the canyon reopening for recreational use in 1975—Salt Lake City needed a new treatment facility to keep clean water flowing. The Salt Lake City Department of Public Utilities (SLCDPU) partnered with engineering firm Brown and Caldwell in design in 2018 to envision and engineer something new to ensure resiliency and reliable water service to its customers. While the plant escaped any critical damage in the March 2020 earthquake, it was a reminder of the urgent need to create a new facility. Design and construction would work around a coterie of barriers and challenges—keeping operations ongoing while building on a challenging site three miles into the wilderness—to produce the future of water treatment for Salt Lake City.

























